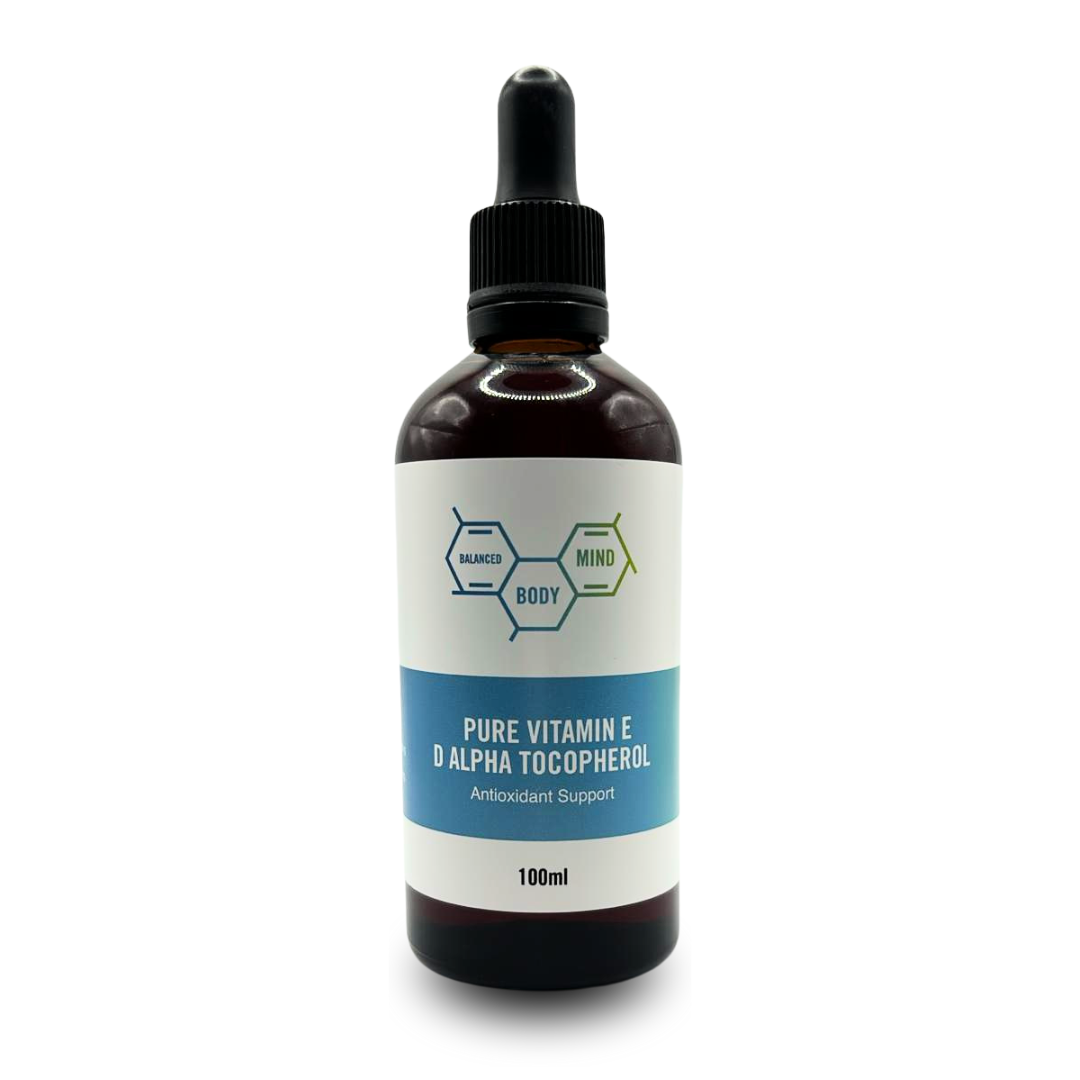
Niacinamide powder 250g
Vitamin B3 is also known as niacin or nicotinic acid and is one of the 8 water-soluble B vitamins. Nicotinamide is derived from Niacin and is used to make NAD (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) Niacin can be synthesised in the liver from the amino acid tryptophan.
Contributes to normal psychological function, including aspects of mental performance such as concentration, learning, memory and reasoning. Combined deficiency of niacin and tryptophan cause the symptoms of pellagra. These are dermatitis, diarrhoea, dementia, depression, apathy, headache, fatigue and memory loss.
Contributes to normal energy yielding metabolism – Energy is generally derived from oxidation/reduction (redox) reactions involving the transfer of electrons. The coenzymes NAD and NADP are required by up to 200 enzymes to give and take electrons for these redox reactions. NAD is needed to break down carbohydrates, fats, proteins and alcohol to provide energy and NADP is needed to synthesise fatty acids and cholesterol. NAD and NADP are also key components of pathways that make more ATP (energy molecules) and ADP –ribose transfer reactions. These reactions are involved in the control of cellular processes such as DNA repair and programmed cell death (apoptosis) So niacin contributes to energy and vitality.
Contributes to the normal functioning of the nervous system
Contributes to the maintenance of normal mucous membranes
Contributes to the maintenance of normal skin
Contributes to the reduction of tiredness and fatigue
Dietary surveys indicate 15-25% of older adults do not consume enough dietary niacin to meet RDA. Dietary intake decreases between 60-90years
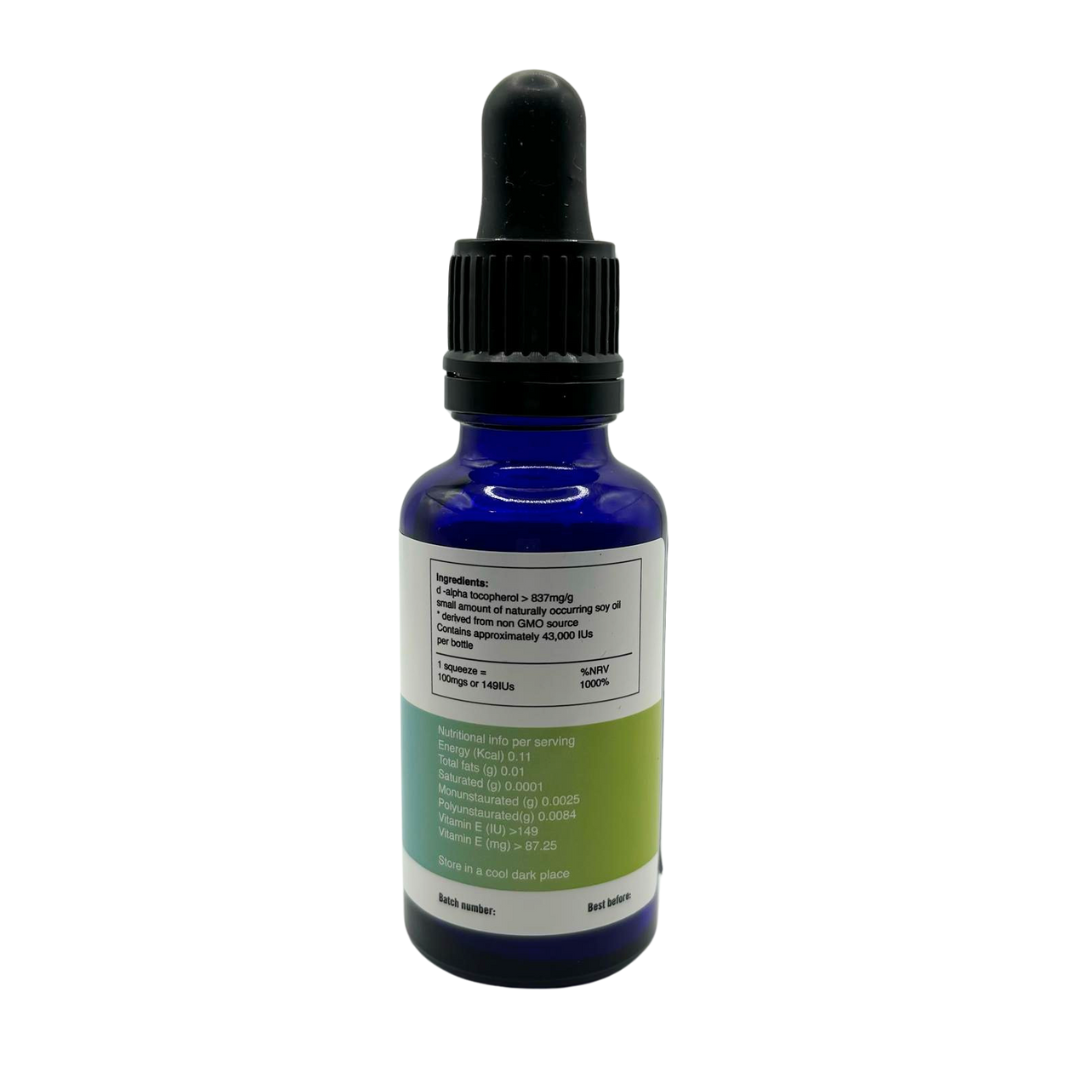
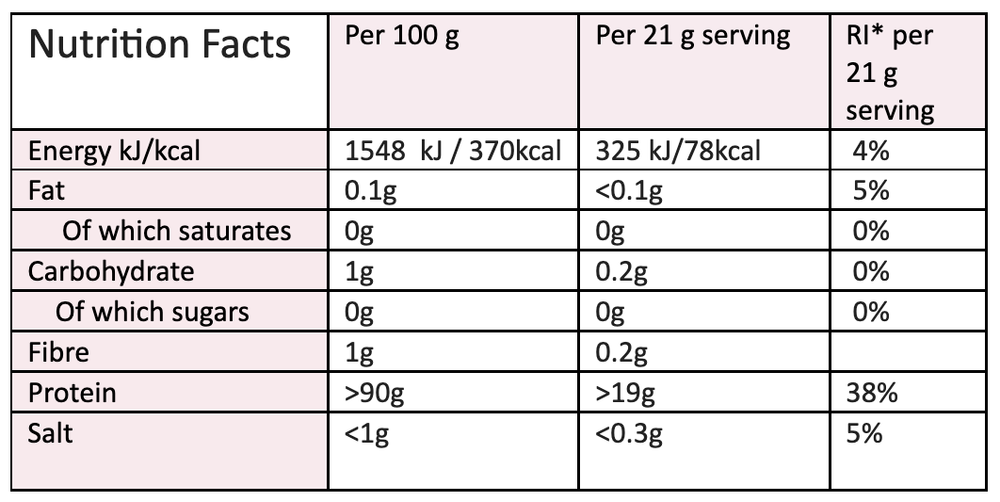
Vitamin B3 is supplied with a scoop of 500mg niacinamide. Much smaller doses can be started by either measuring on a scale or using a 1/5th of the scoop to give 100mgs and should be taken with food.
Vitamin B3 is also known as niacin or nicotinic acid and is one of the 8 water-soluble B vitamins. Nicotinamide is derived from Niacin and is used to make NAD (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) Niacin can be synthesised in the liver from the amino acid tryptophan.
Contributes to normal psychological function, including aspects of mental performance such as concentration, learning, memory and reasoning. Combined deficiency of niacin and tryptophan cause the symptoms of pellagra. These are dermatitis, diarrhoea, dementia, depression, apathy, headache, fatigue and memory loss.
Contributes to normal energy yielding metabolism – Energy is generally derived from oxidation/reduction (redox) reactions involving the transfer of electrons. The coenzymes NAD and NADP are required by up to 200 enzymes to give and take electrons for these redox reactions. NAD is needed to break down carbohydrates, fats, proteins and alcohol to provide energy and NADP is needed to synthesise fatty acids and cholesterol. NAD and NADP are also key components of pathways that make more ATP (energy molecules) and ADP –ribose transfer reactions. These reactions are involved in the control of cellular processes such as DNA repair and programmed cell death (apoptosis) So niacin contributes to energy and vitality.
Contributes to the normal functioning of the nervous system
Contributes to the maintenance of normal mucous membranes
Contributes to the maintenance of normal skin
Contributes to the reduction of tiredness and fatigue
Dietary surveys indicate 15-25% of older adults do not consume enough dietary niacin to meet RDA. Dietary intake decreases between 60-90years
Vitamin B3 is supplied with a scoop of 500mg niacinamide. Much smaller doses can be started by either measuring on a scale or using a 1/5th of the scoop to give 100mgs and should be taken with food.
Vitamin B3 is also known as niacin or nicotinic acid and is one of the 8 water-soluble B vitamins. Nicotinamide is derived from Niacin and is used to make NAD (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) Niacin can be synthesised in the liver from the amino acid tryptophan.
Contributes to normal psychological function, including aspects of mental performance such as concentration, learning, memory and reasoning. Combined deficiency of niacin and tryptophan cause the symptoms of pellagra. These are dermatitis, diarrhoea, dementia, depression, apathy, headache, fatigue and memory loss.
Contributes to normal energy yielding metabolism – Energy is generally derived from oxidation/reduction (redox) reactions involving the transfer of electrons. The coenzymes NAD and NADP are required by up to 200 enzymes to give and take electrons for these redox reactions. NAD is needed to break down carbohydrates, fats, proteins and alcohol to provide energy and NADP is needed to synthesise fatty acids and cholesterol. NAD and NADP are also key components of pathways that make more ATP (energy molecules) and ADP –ribose transfer reactions. These reactions are involved in the control of cellular processes such as DNA repair and programmed cell death (apoptosis) So niacin contributes to energy and vitality.
Contributes to the normal functioning of the nervous system
Contributes to the maintenance of normal mucous membranes
Contributes to the maintenance of normal skin
Contributes to the reduction of tiredness and fatigue
Dietary surveys indicate 15-25% of older adults do not consume enough dietary niacin to meet RDA. Dietary intake decreases between 60-90years
Vitamin B3 is supplied with a scoop of 500mg niacinamide. Much smaller doses can be started by either measuring on a scale or using a 1/5th of the scoop to give 100mgs and should be taken with food.